Random sampling is common in ecology. We often stratify the sample to ensure an equal (or minimum) amount of plots fall within some category (e.g. soils, elevation, cover type, etc.) that is meaningful to the central question of the study. Ecologists often stratify their study area based on landscape facets (Assal et al. 2014). Furthermore, it can be advantageous to use this approach when working with remotely sensed covariates, as segregating the landscape into sub-regions of similar biophysical characteristics can isolate spectral gradients (Homer et al. 2004).
This can be accomplished very efficiently using a raster-based approach in R. In this example, I will randomly sample 5 cells in three strata, then obtain the coordinates of the cell centroid and convert the points to a SpatialPointsDataFrame using the raster library. The code below is very basic, but it can be modified to work with any discrete raster that represents the complex landscape facets of interest.
######
# load R logo as base raster
######
library(raster)
logo <- raster(system.file("external/rlogo.grd", package="raster"))
logo
plot(logo)
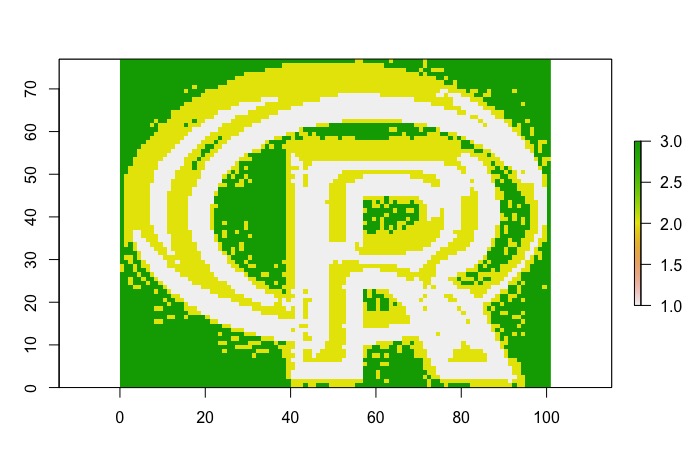
######
# reclassify into three levels based on quantiles
######
quantile(logo, c(0.33)) #get 33rd percentile
quantile(logo, c(0.66)) #get 66th percentile
#classify into three strata based on 33rd and 66th quantiles
logo.rc<-reclassify(logo, c(-Inf,quantile(logo, c(0.33)),1, quantile(logo, c(0.33)),quantile(logo, c(0.66)),2, quantile(logo, c(0.66)),Inf,3))
plot(logo.rc)
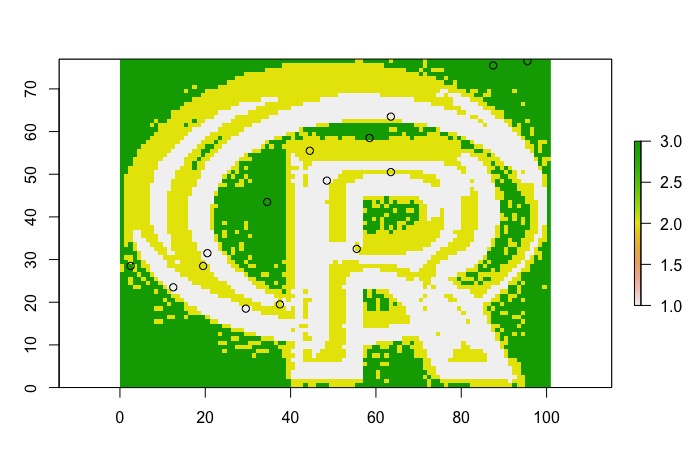
######
# conduct stratified random sample
######
names(logo.rc) <- 'stratum'
#select 5 cells from each of the 3 stratums; total of 15 samples
sample.cells<-sampleStratified(logo.rc, size=5) #result is a matrix with cell number and stratum code
#convert from matrix to DF
sample.cells.DF<-as.data.frame(sample.cells)
#get lat long of cell centroids
sample.coords<-xyFromCell(logo.rc, sample.cells.DF[,1])
#convert from matrix to DF
sample.coords.DF<-as.data.frame(sample.coords)
#merge dataframes
sample.out<-cbind(sample.coords.DF, sample.cells.DF)
#promote to spatialpointsdataframe
coordinates(sample.out) = c("x", "y")
#add points to plot
points(sample.out)
Literature Cited
Assal, T.J., Sibold, J., and R. Reich. 2014. Modeling a Historical Mountain Pine Beetle Outbreak Using Landsat MSS and Multiple Lines of Evidence. Remote Sensing of Environment 155:275-288.
Homer, C., Huang, C., Yang, L., Wylie, B., & Coan, M. 2004. Development of a 2001 National Land-Cover Database for the United States. Photogrammetric Engineering & Remote Sensing 70:829-840.
